在开发功能灵活的Nginx模块时,需要从配置文件中获取特定的信息。不过,我们并不需要再编写一套读取配置的系统,Nginx已经为用户提供了强大的配置项解析机制,同时还支持“-s reload”命令,可以在不重启服务的情况下可使配置生效。
一、Nginx配置文件简介
如果编译安装Nginx时使用默认路径,那么Nginx运行目录是/usr/local/nginx,其配置文件存放目录是/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。其内容默认如下:
块配置项
配置文件中有很多块配置项。块配置项是由一个块配置项名和一对大括号组成。例如上面代码段中的http、server、event等等。也可以在块配置项名之后后大括号之前加上参数。
块配置项可以嵌套。内层块直接继承外层块。例如上例中server块里的任意配置都是基于http块里的已有配置的。当内外层中的配置发生冲突时,究竟是以内层块还是外层块的配置为准取决于解析这个配置项的模块。
配置项的语法
最基本的配置项语法格式:
配置项名 配置项值1 配置项值2 配置项值3 ... ;
行首是配置项名,这些配置项名必须是Nginx的某一个模块想要处理的,否则Nginx会认为配置文件出现了非法的配置项名。配置项名输入结束后以空格作为分隔符。
其次是配置项值,可以是数字或字符串。可以由一个或多个配置项值。中间以空格分隔。
最后,行尾是分号。
以“#”开始的是注释行。
二、怎样使用http配置
处理http配置项可以分为以下四个步骤:
(1)创建数据结构用于存储配置项对应的参数。
(2)设定配置项在nginx.conf中出现时的限制条件与回调方法。
(3)实现第二步中的回调方法,或者使用Nginx框架预设的14个回调方法。
(4)合并不同级别的配置块中出现的同名配置项。
在这里不得不提到的是两个非常重要的数据结构:ngx_http_module_t以及ngx_command_t,是HTTP模块时不可或缺的部分,它们把这四个步骤与Nginx有机地结合起来。
在本例中我们通过在配置文件中添加如下项来自己编写模块进行解析(添加到默认server块内):
#测试配置项2
location /test2 {
test_str "hello my dear HUST!";
test_flag on;
test_num 10;
test_size 1000;
mytest;
}
要实现的效果是,当在浏览器中输入http://localhost/test2时,将所有包含参数的配置项名及其对应的参数输出。分配用于保存配置参数的数据结构
这个数据结构依据需要保存的参数自定义即可。
一般情况下这个结构是(包含了各种类型的配置项,但是在本例中只实现了部分类型的配置项的解析):
typedef struct{
ngx_str_t arg_str;
ngx_int_t arg_num;
ngx_flag_t arg_flag;
size_t arg_size;
ngx_array_t* arg_str_array;
ngx_array_t* arg_keyval;
off_t arg_off;
ngx_msec_t arg_msec;
time_t arg_sec;
ngx_bufs_t arg_bufs;
ngx_uint_t arg_enum_seq;
ngx_uint_t arg_bitmask;
ngx_uint_t arg_access;
ngx_path_t* arg_path;
}ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t;
需要注意的是,这个结构会Nginx的内存中保存许多份。http框架在解析nginx.conf文件时,只要遇到http{}、server{}、或者location{}配置块就会立刻分配一个新的结构体。
Nginx如何管理我们自定义的存储配置的结构体呢?
是通过ngx_http_module_t中的8个回调方法(ngx_http_config.h):
24 typedef struct {
25 ngx_int_t (*preconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
26 ngx_int_t (*postconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
27
28 void *(*create_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
29 char *(*init_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *conf);
30
31 void *(*create_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
32 char *(*merge_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
33
34 void *(*create_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
35 char *(*merge_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
36 } ngx_http_module_t;
其中以create开头的三个回调方法负责把我们分配的用于保存配置项的结构体传递给http框架。为什么会定义三个回调方法呢?
http框架定义了三个级别的配置main、srv、loc,分别表示直接出现在http{}、server{}、location{}、块内的配置。当nginx.conf中出现http{}时,http框架会接管配置文件中http{}块内的配置项解析。当遇到http{}配置块时,http框架会调用所有的http模块可能实现的create_main_conf、create_srv_conf、create_loc_conf方法生成存储main级别的配置参数的结构体;在遇到server{}配置块时,会再次调用所有的http模块可能实现的create_srv_conf、create_loc_conf方法生成存储srv级别的配置参数的结构体;在遇到location{}配置块时,会再次调用所有的http模块可能实现的create_loc_conf方法生成存储loc级别的配置参数的结构体。实现三个回调方法的意义是不同的。在一个模块中,http块内只会调用一次create_main_conf,但是create_loc_conf可能会被调用很多次,也就是有许多由create_loc_conf生成的结构体。
普通http请求往往只实现create_loc_conf回调方法,因为它们只关注匹配某种URL的请求。
设定配置项的解析方式
我们在ngx_command_t结构体中设定配置项的解析方式:
78 struct ngx_command_s {
79 ngx_str_t name;
80 ngx_uint_t type;
81 char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
82 ngx_uint_t conf;
83 ngx_uint_t offset;
84 void *post;
85 };
在本例中,前四个配置项都用预设的方法进行解析,而最后一个配置项mytest用自定义的方法,并在这个方法中将前面各个配置项的参数组合成一个字符串返回给客户。
我们需要通过定义ngx_command_t数组来设置配置项的解析方式:
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest2_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("test_str"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_str),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_flag"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_flag),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_num"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_num_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_num),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_size"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_size_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_size),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("mytest"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_mytest2,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
0,
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
其中自定义的配置项解析方法ngx_http_mytest2:
static char *
ngx_http_mytest2(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_mytest2_handler;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
真正完成处理工作的handler是 ngx_http_mytest2_handler:
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mytest2_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t *elcf;
elcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r,ngx_http_mytest2_module);
if (!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_GET | NGX_HTTP_HEAD | NGX_HTTP_POST))) {
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
ngx_int_t rc = ngx_http_discard_request_body(r);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
ngx_str_t type = ngx_string("text/plain");
ngx_str_t str_format = ngx_string("test_str=%V,test_flag=%i,test_num=%i,test_size=%z");
ngx_str_t test_str = elcf->arg_str;
ngx_flag_t test_flag = elcf->arg_flag;
ngx_int_t test_num = elcf->arg_num;
size_t test_size = elcf->arg_size;
int data_len = str_format.len + test_str.len + 1;
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = data_len;
r->headers_out.content_type = type;
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->header_only) {
return rc;
}
ngx_buf_t *b;
b = ngx_create_temp_buf(r->pool,data_len);
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
ngx_snprintf(b->pos,data_len,(char *)str_format.data,&test_str,test_flag,test_num,test_size);
b->last = b->pos + data_len;
b->last_buf = 1;
ngx_chain_t out;
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
三、新添加模块的编译
普通编译方式是:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --add-module=XX(新模块的config文件以及源码所存放的目录)
make
sudo make install
但是这样的一个缺点是:每次都要编译所有的nginx源码,速度慢。如果自己编写的新模块中的源代码中有错误,调试起来很不方便。有一个方法是自己编写一个makefile文件,先单独编译新模块的代码,修正所有错误之后再将其编译进Nginx。
这是我编写的MakeFile文件:
#编译新模块的makefile文件
ngx_http_mytest_module.o: ngx_http_mytest_module.c
gcc -c -pipe -O -W -Wall -Wpointer-arith -Wno-unused-parameter -Werror -g -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/core -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/event -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/event/modules -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/os/unix -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/objs -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/http -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/http/modules -I /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/src/mail -o ngx_http_mytest_module.o /home/xiajun/TEST/Nginx/nginx-1.4.1/mytest/ngx_http_mytest_module.c
四、完整代码及结果演示
config文件:
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http_mytest2
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES ngx_http_mytest2_module"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http_mytest2_module.c"
ngx_http_mytest2_module.c:
#include <ngx_config.h>
#include <ngx_core.h>
#include <ngx_http.h>
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_mytest2_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r);
static char *
ngx_http_mytest2(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
static void*
ngx_http_mytest2_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static char*
ngx_http_mytest2_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf,void *parent,void *child);
typedef struct{
ngx_str_t arg_str;
ngx_int_t arg_num;
ngx_flag_t arg_flag;
size_t arg_size;
ngx_array_t* arg_str_array;
ngx_array_t* arg_keyval;
off_t arg_off;
ngx_msec_t arg_msec;
time_t arg_sec;
ngx_bufs_t arg_bufs;
ngx_uint_t arg_enum_seq;
ngx_uint_t arg_bitmask;
ngx_uint_t arg_access;
ngx_path_t* arg_path;
}ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t;
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_mytest2_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("test_str"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_str_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_str),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_flag"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_flag_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_flag),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_num"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_num_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_num),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("test_size"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_size_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t,arg_size),
NULL
},
{
ngx_string("mytest"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LMT_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_mytest2,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
0,
NULL
},
ngx_null_command
};
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_mytest2_module_ctx = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
ngx_http_mytest2_create_loc_conf,
ngx_http_mytest2_merge_loc_conf
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_mytest2_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_mytest2_module_ctx,
ngx_http_mytest2_commands,
NGX_HTTP_MODULE,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
static char *
ngx_http_mytest2(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_mytest2_handler;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_mytest2_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t *elcf;
elcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r,ngx_http_mytest2_module);
if (!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_GET | NGX_HTTP_HEAD | NGX_HTTP_POST))) {
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
ngx_int_t rc = ngx_http_discard_request_body(r);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
ngx_str_t type = ngx_string("text/plain");
ngx_str_t str_format = ngx_string("test_str=%V,test_flag=%i,test_num=%i,test_size=%z");
ngx_str_t test_str = elcf->arg_str;
ngx_flag_t test_flag = elcf->arg_flag;
ngx_int_t test_num = elcf->arg_num;
size_t test_size = elcf->arg_size;
int data_len = str_format.len + test_str.len + 1;
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = data_len;
r->headers_out.content_type = type;
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->header_only) {
return rc;
}
ngx_buf_t *b;
b = ngx_create_temp_buf(r->pool,data_len);
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
ngx_snprintf(b->pos,data_len,(char *)str_format.data,&test_str,test_flag,test_num,test_size);
b->last = b->pos + data_len;
b->last_buf = 1;
ngx_chain_t out;
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
static void*
ngx_http_mytest2_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf){
ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool,sizeof(ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t));
if(NULL == conf){
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
conf->arg_str.len = 0;
conf->arg_str.data = NULL;
conf->arg_flag = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
conf->arg_num = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
conf->arg_str_array = NGX_CONF_UNSET_PTR;
conf->arg_keyval = NULL;
conf->arg_off = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
conf->arg_msec = NGX_CONF_UNSET_MSEC;
conf->arg_sec = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
conf->arg_size = NGX_CONF_UNSET_SIZE;
return conf;
}
static char*
ngx_http_mytest2_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf,void *parent,void *child){
ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t *prev = parent;
ngx_http_mytest2_loc_conf_t *conf = child;
ngx_conf_merge_str_value(conf->arg_str,prev->arg_str,"");
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
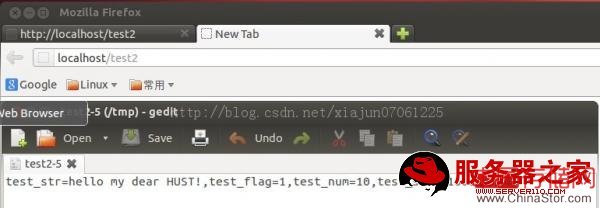
结果演示: