可能是对 Ngixn资源不熟悉,干脆就直接读源码,分析出支持的变量。
Nginx支持的http变量实现在 ngx_http_variables.c 的 ngx_http_core_variables存储实现:
ngx_http_core_variables
1 static ngx_http_variable_t ngx_http_core_variables[] = {
2
3 { ngx_string("http_host"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
4 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.host), 0, 0 },
5
6 { ngx_string("http_user_agent"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
7 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.user_agent), 0, 0 },
8
9 { ngx_string("http_referer"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
10 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.referer), 0, 0 },
11
12 #if (NGX_HTTP_GZIP)
13 { ngx_string("http_via"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
14 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.via), 0, 0 },
15 #endif
16
17 #if (NGX_HTTP_PROXY || NGX_HTTP_REALIP)
18 { ngx_string("http_x_forwarded_for"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
19 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.x_forwarded_for), 0, 0 },
20 #endif
21
22 { ngx_string("http_cookie"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_headers,
23 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.cookies), 0, 0 },
24
25 { ngx_string("content_length"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
26 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.content_length), 0, 0 },
27
28 { ngx_string("content_type"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_header,
29 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_in.content_type), 0, 0 },
30
31 { ngx_string("host"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_host, 0, 0, 0 },
32
33 { ngx_string("binary_remote_addr"), NULL,
34 ngx_http_variable_binary_remote_addr, 0, 0, 0 },
35
36 { ngx_string("remote_addr"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_remote_addr, 0, 0, 0 },
37
38 { ngx_string("remote_port"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_remote_port, 0, 0, 0 },
39
40 { ngx_string("server_addr"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_server_addr, 0, 0, 0 },
41
42 { ngx_string("server_port"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_server_port, 0, 0, 0 },
43
44 { ngx_string("server_protocol"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request,
45 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, http_protocol), 0, 0 },
46
47 { ngx_string("scheme"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_scheme, 0, 0, 0 },
48
49 { ngx_string("request_uri"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request,
50 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, unparsed_uri), 0, 0 },
51
52 { ngx_string("uri"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request,
53 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, uri),
54 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
55
56 { ngx_string("document_uri"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request,
57 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, uri),
58 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
59
60 { ngx_string("request"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request_line, 0, 0, 0 },
61
62 { ngx_string("document_root"), NULL,
63 ngx_http_variable_document_root, 0, NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
64
65 { ngx_string("realpath_root"), NULL,
66 ngx_http_variable_realpath_root, 0, NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
67
68 { ngx_string("query_string"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_request,
69 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, args),
70 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
71
72 { ngx_string("args"),
73 ngx_http_variable_request_set,
74 ngx_http_variable_request,
75 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, args),
76 NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE|NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
77
78 { ngx_string("is_args"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_is_args,
79 0, NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
80
81 { ngx_string("request_filename"), NULL,
82 ngx_http_variable_request_filename, 0,
83 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
84
85 { ngx_string("server_name"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_server_name, 0, 0, 0 },
86
87 { ngx_string("request_method"), NULL,
88 ngx_http_variable_request_method, 0,
89 NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
90
91 { ngx_string("remote_user"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_remote_user, 0, 0, 0 },
92
93 { ngx_string("body_bytes_sent"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_body_bytes_sent,
94 0, 0, 0 },
95
96 { ngx_string("request_completion"), NULL,
97 ngx_http_variable_request_completion,
98 0, 0, 0 },
99
100 { ngx_string("request_body"), NULL,
101 ngx_http_variable_request_body,
102 0, 0, 0 },
103
104 { ngx_string("request_body_file"), NULL,
105 ngx_http_variable_request_body_file,
106 0, 0, 0 },
107
108 { ngx_string("sent_http_content_type"), NULL,
109 ngx_http_variable_sent_content_type, 0, 0, 0 },
110
111 { ngx_string("sent_http_content_length"), NULL,
112 ngx_http_variable_sent_content_length, 0, 0, 0 },
113
114 { ngx_string("sent_http_location"), NULL,
115 ngx_http_variable_sent_location, 0, 0, 0 },
116
117 { ngx_string("sent_http_last_modified"), NULL,
118 ngx_http_variable_sent_last_modified, 0, 0, 0 },
119
120 { ngx_string("sent_http_connection"), NULL,
121 ngx_http_variable_sent_connection, 0, 0, 0 },
122
123 { ngx_string("sent_http_keep_alive"), NULL,
124 ngx_http_variable_sent_keep_alive, 0, 0, 0 },
125
126 { ngx_string("sent_http_transfer_encoding"), NULL,
127 ngx_http_variable_sent_transfer_encoding, 0, 0, 0 },
128
129 { ngx_string("sent_http_cache_control"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_headers,
130 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, headers_out.cache_control), 0, 0 },
131
132 { ngx_string("limit_rate"), ngx_http_variable_request_set_size,
133 ngx_http_variable_request_get_size,
134 offsetof(ngx_http_request_t, limit_rate),
135 NGX_HTTP_VAR_CHANGEABLE|NGX_HTTP_VAR_NOCACHEABLE, 0 },
136
137 { ngx_string("nginx_version"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_nginx_version,
138 0, 0, 0 },
139
140 { ngx_string("hostname"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_hostname,
141 0, 0, 0 },
142
143 { ngx_string("pid"), NULL, ngx_http_variable_pid,
144 0, 0, 0 },
145
146 { ngx_null_string, NULL, NULL, 0, 0, 0 }
147 };
把这些变量提取下,总结如下:
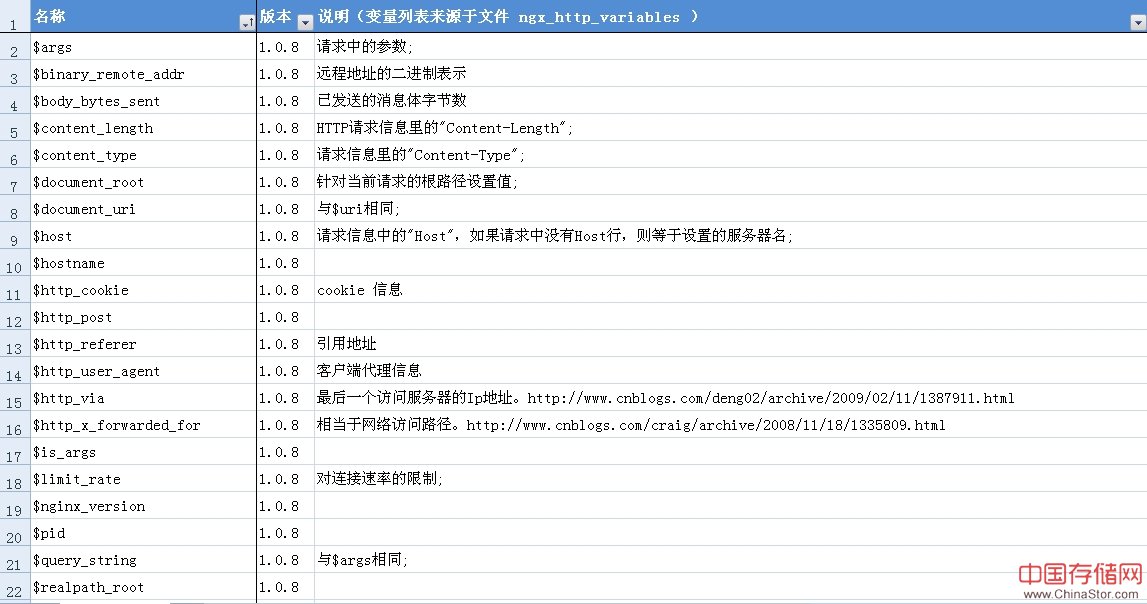
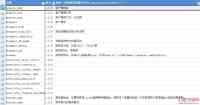

nginx防DDOS攻击的简单配置
nginx本身就有防DDOS攻击这方面的模块ngx_http_limit_req_module和ngx_http_limit_conn_module。
一、基本介绍
1.ngx_http_limit_req_module
配置格式及说明:
设置一个缓存区保存不同key的状态,这里的状态是指当前的过量请求数。而key是由variable指定的,是一个非空的变量,我们这里使用$binary_remote_addr,表示源IP为key值。
limit_req_zone $variable zone=name:size rate=rate;
指定要进行限制的缓存区和最大的请求到达后有多少个请求放入延迟队列(其它的直接丢弃)。如果不希望请求数达到上限而被延迟,就需要使用nodelay。
limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay];
例子:
缓存区为10M,请求限制为每秒1次,延迟队列为5
http {
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s;
...
server {
...
location /search/ {
limit_req zone=one burst=5;
}
}
2.ngx_http_limit_conn_module
配置格式及说明:
设置一个缓存区保存不同key的状态。我们这里使用源IP来作为key,以此限制每个源IP的链接数
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
指定限制的缓存区,并指定每个key的链接个数
limit_conn zone number;
例子:
http {
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
...
server {
...
location /download/ {
limit_conn addr 1;
}
}
二、实际应用
如果作为代理服务器,我们需要限制每个用户的请求速度和链接数量,但是,由于一个页面有多个子资源,如果毫无选择的都进行限制,那就会出现很多不必要的麻烦,如:一个页面有40个子资源,那么如果想让一个页面完整的显示,就需要将请求速度和连接数都调整到40,以此达到不阻塞用户正常请求,而这个限制,对服务器性能影响很大,几百用户就能把一台nginx的处理性能拉下来。
所以我们需要制定哪些请求是需要进行限制的,如html页面;哪些是不需要限制的,如css、js、图片等,这样就需要通过配置对应的location进一步细化。
我们不对css、js、gif、png,jpg等进行连接限制,而对除此之外的链接进行限制
http {
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=5r/s;
...
server {
...
location ~ .*.(gif|png|css|js|icon)$ {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
location ~* .*.(jpeg|jpg|JPG)$ {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
# image_filter resize 480 -;
# image_filter_jpeg_quality 50;
# image_filter_sharpen 10;
# image_filter_buffer 4M;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real_IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#limit
limit_conn addr 3;
limit_req zone=one burst=5;
}
}
Location配置简单介绍:
语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
= 开头表示精确匹配
^~ 开头表示uri以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url路径即可。nginx不对url做编码,因此请求为/static/20%/aa,可以被规则^~ /static/ /aa匹配到(注意是空格)。
~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~和!~*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。